Introduction¶
Examples are available by executing the demo script.
# windows
C:\Python2.7\Scripts\occmodeldemo.py
# linux
occmodeldemo.py
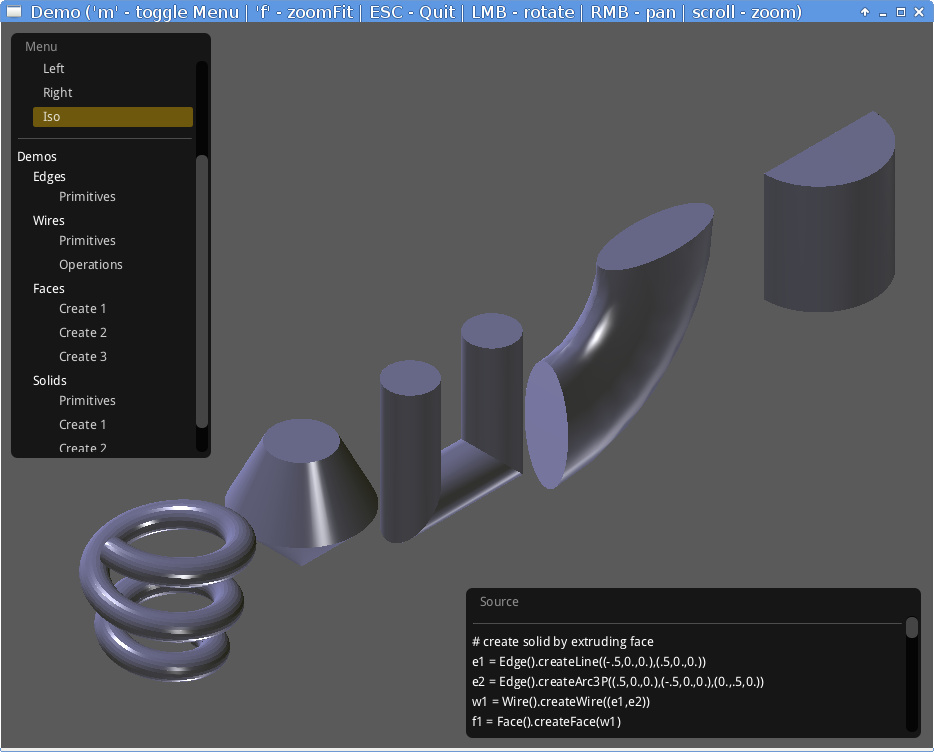
Demo window including GUI elements.
To view geometrical objects simply pass a sequece of object or a single object to the viewer function.
from occmodelviewer import viewer
viewer(solid)
viewer((solid,face,edge))
The viewer can also be used interactive from the Python command prompt. Note that a reference must be keept of the returned Viewer to avoid beeing reclaimed by the garbage collector.
from occmodelviewer import viewer
view = viewer(interactive = True)
view.add(solid)
view.redraw()
It is also possible to read objects from a STEP or BREP file and view the imported geometry.
from occmodel import Tools
from occmodelviewer import viewer
objects = Tools.readSTEP('example.stp')
viewer(objects)
Geometry¶
occmodel.Vertex are 3d points which are used to reference start, end or seam points of edges..
occmodel.Edge are 3d curve which are combined into wires.
occmodel.Wire are composite curves created from edges defining boundaries of faces.
occmodel.Face are underlying surface geometry which are constrained by wires.
occmodel.Solid are the main object which contain rich functionalty to combine and edit solid objects.
Point and vectors passed to the geometry functions can be any valid python sequence of three numbers.
Edges¶
Arc 3P¶
Create an arc Edge defined by three points.
e1 = Edge().createArc3P(start = (1.,0.,0.), end = (-1.,0.,0.), pnt = (0.,1.,0.))
Circle¶
Create circle Edge
e1 = Edge().createCircle(center=(0.,0.,0.),normal=(0.,0.,1.),radius = 1.)
Bezier¶
Create bezier Edge
start = Vertex(0.,0.,0.)
end = Vertex(1.,0.,0.)
pnts = ((0.,2.,0.), (1.,1.5,0.))
e1 = Edge().createBezier(start,end,pnts)
Spline¶
Create a spline Edge
start = Vertex(0.,0.,0.)
end = Vertex(1.,0.,0.)
pnts = ((0.,2.,0.), (5.,1.5,0.))
e1 = Edge().createSpline(start,end,pnts)
Faces¶
Face interior point¶
Create face from circle edge and interior point.
e1 = Edge().createCircle(center=(0.,0.,0.),normal=(0.,0.,1.),radius = 1.)
f1 = Face().createConstrained(e1, ((0.,.5,.25),))
Face edge sequence¶
Create face from sequence of edges.
start = Vertex(1.,0.,0.)
end = Vertex(-1.,0.,0.)
e1 = Edge().createLine(end,start)
pnt = (0.,1.,0.)
e2 = Edge().createArc3P(start,end,pnt)
w1 = Wire().createWire((e1,e2))
f1 = Face().createFace(w1)
Polygonal face¶
Create a planar polygonal face
pnts = ((0.,0.,0.), (0.,2.,0.), (1.,2.,0.), (1.,0.,0.))
f1 = Face().createPolygonal(pnts)
Solids¶
Primitive Solids¶
Create sphere primitive.
solid = Solid()
solid.createSphere((1.,2.,3.),.5)
Create box primitive.
solid = Solid().createBox((0.,0.,0.),(100.,100.,100.))
Create cylinder primitive.
solid = Solid().createCylinder((0.,0.,0.),(0.,0.,1.), 1.)
Create torus primitive.
solid = Solid().createTorus((0.,0.,0.),(0.,0.,1.), 1., 2.)
Create cone primitive.
solid = Solid().createCone((0.,0.,0.),(0.,0.,1.), 1., 2.)
Boolean¶
Boolean union between two solid spheres.
s1 = Solid().createSphere((0.,0.,0.),.5)
s2 = Solid().createSphere((.25,0.,0.),.5)
s1.fuse(s2)
Boolean difference between two solid spheres.
s1 = Solid().createSphere((0.,0.,0.),.5)
s2 = Solid().createSphere((.25,0.,0.),.5)
s1.cut(s2)
Boolean intersection between two solid spheres.
s1 = Solid().createSphere((0.,0.,0.),.5)
s2 = Solid().createSphere((.25,0.,0.),.5)
s1.common(s2)
Extrude¶
Extrude face along vector.
pnts = (
(0.,0.,0.),
(0.,2.,0.),
(5.,1.5,0.),
(0.,0.,0.)
)
e1 = Edge().createSpline(points = pnts)
face = Face().createFace(e1)
solid = Solid().extrude(face, (0.,0.,0.), (0.,0.,5.))
Revolve¶
Revolve face to create solid.
e1 = Edge().createCircle(center=(0.,0.,0.),normal=(0.,0.,1.),radius = 1.)
face = Face().createFace(e1)
solid = Solid().revolve(face, (0.,2.,0.), (1.,2.,0.), pi/2.)
Loft¶
Loft through edges.
e1 = Edge().createCircle(center=(0.,0.,0.),normal=(0.,0.,1.),radius = 1.)
e2 = Edge().createEllipse(center=(0.,0.,5.),normal=(0.,0.,1.), rMajor = 2.0, rMinor=1.0)
e3 = Edge().createCircle(center=(0.,0.,10.),normal=(0.,0.,1.),radius = 1.0)
solid = Solid().loft((e1,e2,e3))
Pipe¶
Extrude circle along arc edge
e1 = Edge().createArc((0.,0.,0.),(2.,0.,2.),(2.,0.,0.))
e2 = Edge().createCircle(center=(0.,0.,0.),normal=(0.,0.,1.),radius = 1.)
f1 = Face().createFace(e2)
solid = Solid().pipe(f1, e1)
Advanced solids¶
Create open box with fillet edges.
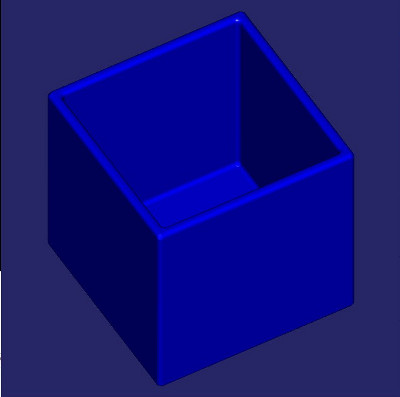
Box example plot.
solid = Solid().createBox((0.,0.,0.),(100.,100.,100.))
for face in FaceIterator(solid):
bbox = face.boundingBox()
if bbox.near.z > 50. and bbox.far.z > 50.:
break
solid.shell(-5., face)
solid.fillet(2.)
Union of cyllinders with fillet intersection edge.
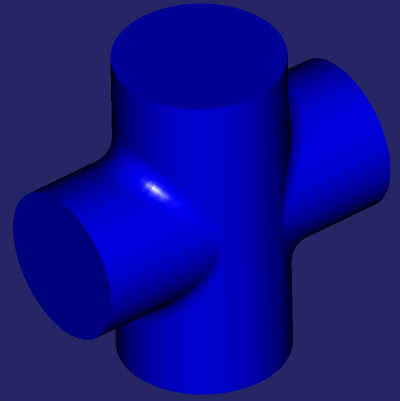
Cylinder example plot.
s1 = Solid().createCylinder((0.,0.,-2.),(0.,0.,2.), 1.)
s2 = Solid().createCylinder((0.,-2.,0.),(0.,2.,0.), .9)
s1.fuse(s2)
edges = []
origo = Point(0.,0.,0.)
for edge in EdgeIterator(s1):
bbox = edge.boundingBox()
if bbox.near.distanceTo(origo) < 1.75:
if bbox.far.distanceTo(origo) < 1.75:
edges.append(edge)
s1.fillet(0.3, edges)
Construc bowl like solid.
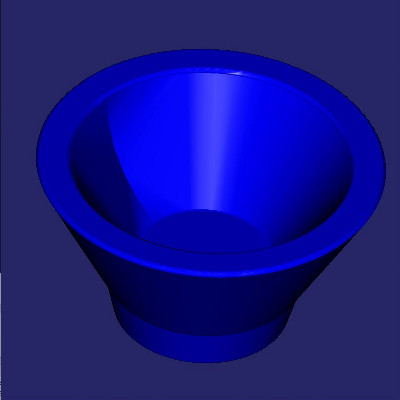

Bowl example plot.
# cut sphere in half
solid = Solid().createSphere((0.,0.,0.),10.)
box = Solid().createBox((-11.,-11.,0.),(11.,11.,11.))
solid.cut(box)
# shell operation
face = None
for face in FaceIterator(solid):
bbox = face.boundingBox()
if bbox.near.z > -1. and bbox.far.z > -1.:
break
solid.shell(-2., face)
# foot
cone = Solid().createCone((0.,0.,-11.), (0.,0.,-7.), 5., 6.)
solid.fuse(cone)
# fillet all edges
solid.fillet(.25)